This is the sixth in a series of short biographies of persons whose names are directly used for diseases, conditions or syndromes familiar to those in clinical pathology laboratories.
Guillaume Duchenne (1806–1875) was born in Boulogne-Sur-Mer, a harbour city in the coastal region of Northern France, to a humble provincial family with a seafaring history. In 1827, against his father’s wishes and driven by an interest in science, he began medical studies in Paris and qualified in 1831. Duchenne trained under a number of noted Paris physicians, including Rene Laennec.
He returned to his home city to practise general medicine and married, but his wife died two weeks after giving birth to their son. In a difficult period of his life, he became estranged from his son and suffered bouts of depression. However, he did perform some preliminary research on electrophysiology from 1833 using an electropuncture technique based on the earlier research of the Italian physician Luigi Galvani.
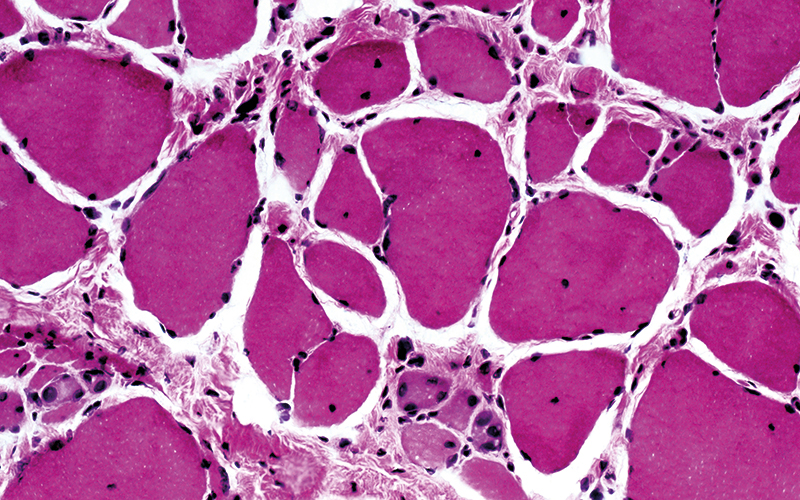
Duchenne returned to Paris in 1842 and established a small private practice. He was a regular visitor to the teaching hospitals of Paris, notably the Pitie-Salpetriere Hospital, which had a psychiatric unit with a large number of patients with neuromuscular diseases, and he developed a career-long interest for rare and unusual neurological cases. He had persistent and meticulously recorded observation, combined with the use of instruments he designed for diagnostic investigation, notably a portable electrical device to apply faradic stimulation to the skin surface to map neural pathways through muscle contraction in health and disease. He also designed the “Duchenne harpoon” to collect percutaneous tissue for microscopy – an early example of biopsy procedure...
Please click here to read the full article.
Image credit | Science-Photo-Library | Alamy