A national trial has launched that aims to use pandemic lessons to help quickly find effective treatments for people hospitalised with severe flu.
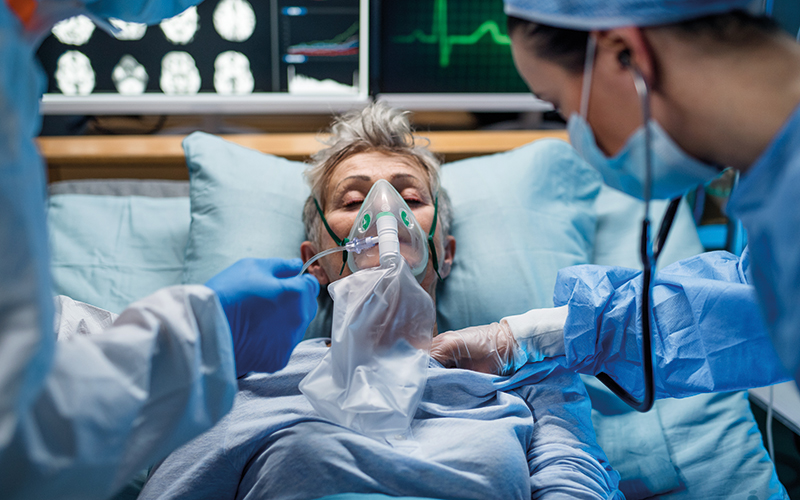

The £2.9m REMAP-CAP trial will recruit children and adults hospitalised with severe flu from 150 hospitals across the UK over the next two years.
It will be run by researchers and clinicians from Imperial College London and Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust in collaboration with other national experts. It is the first time a trial of this kind will be used for flu.
The REMAP-CAP trial was originally set up to tackle pandemics. It is exactly two years since REMAP-CAP showed in COVID-19 how reducing inflammation with the drug tocilizumab can save lives in severely ill patients.
The trial is designed to provide answers quickly by using a robust yet rapid approach to test multiple treatments at the same time in thousands of people.
Professor Anthony Gordon, Chief Investigator, said: “Flu is very infectious and can make children, the elderly and vulnerable people seriously unwell in some cases.
“This winter, we might see more flu cases than usual as the virus potentially resurges after pandemic measures have kept levels low. We hope that our trial will help to find urgently needed flu treatments rapidly. Our COVID-19 trial changed clinical practice globally, and we hope we can impact flu treatment and reduce winter pressures on the NHS in the same way.”
Image credit | Shutterstock