Research from UC Davis Health explores how differences in skin composition may lead to dermatological conditions, such as psoriasis and atopic dermatitis.
Emanual Maverakis, Professor of Dermatology, Molecular Medical Microbiology at UC Davis, said: “Different skin characteristics at different body sites may affect the skin’s susceptibility to certain diseases.”
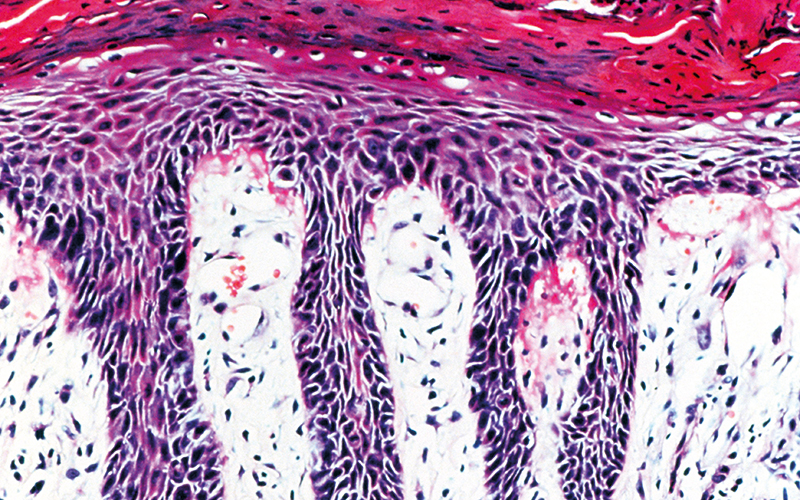
The team used single-cell sequencing to characterise how the keratinocytes differ at different body sites. They also used targeted molecular profiling to characterise the molecules that form the “mortar” between the keratinocytes.
They then examined how these differences in gene expression matched the compositional differences in the lipid and protein structures across body sites.
These experiments showed why the skin looks so different at different sites.
The compositional differences in the skin’s lipids and proteins across different body sites may also explain why different skin diseases are found at different body sites.
While characterising the specific lipid alterations associated with various skin diseases, the researchers discovered that lipids stuck to a piece of tape applied to the skin were sufficient to diagnose a patient with a particular skin disease.
“These discoveries will lead to non-diagnostic tests for common dermatologic disease” said co-lead author, Project Scientist Alexander Merleev.
Image Credit | Science-Photo-Library