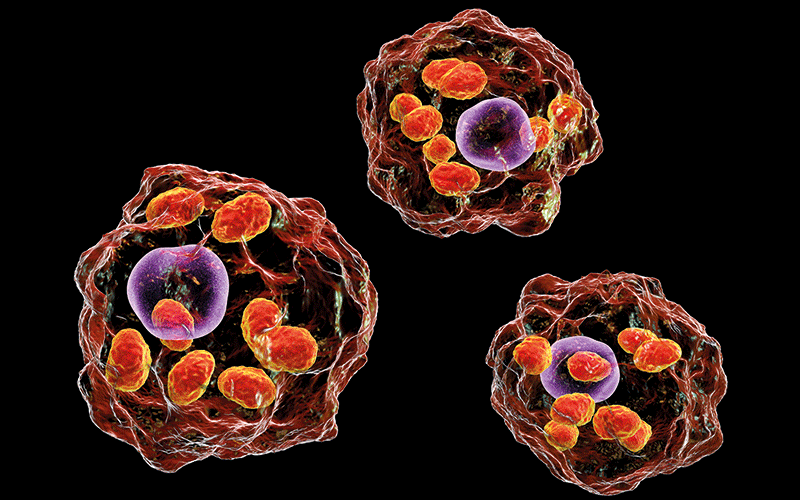
Brazilian researchers have demonstrated protozoans of the genus Leishmania that cause leishmaniasis manipulate a protein that plays an essential role in the organism’s defence in order to continue to replicate, preventing the body from vanquishing the disease.
The findings of the study offer hope for the development of novel treatments for the disease. Some 30,000 new cases of leishmaniasis are recorded annually, according to the World Health Organization and there are no specific medications or vaccines to combat the disease.
The protein is gasdermin-D, produced by macrophages and other cells in the immune system.
“Gasdermin-D is important to activation of the inflammasome, a complex of proteins involved in the organism’s defence against infection. We observed activation of the inflammasome in biopsies from patients with tegumental leishmaniasis [comprising the cutaneous and mucocutaneous forms],” said Keyla de Sá, first author of the article.
The team from the University of São Paulo showed that the parasite manages to bring about alternative cleavage of gasdermin-D, changing the protein’s structural form and inactivating it so that it cannot perform its inflammatory functions.
Image credit | Getty