Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) evaluated several human antibodies to determine the most potent combination to be mixed in a cocktail and used as a promising anti-viral therapy against the virus that causes COVID-19.
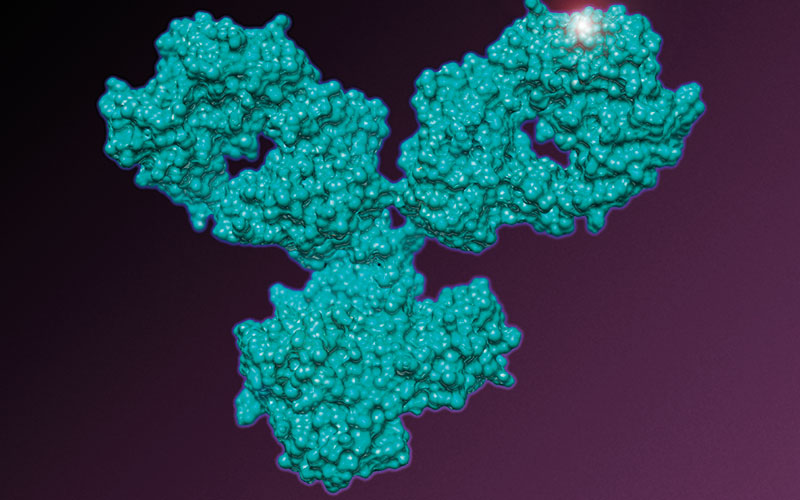
The study demonstrates the rapid process of isolating, testing and mass-producing antibody therapies against any infectious disease by using both genetically engineered mice and plasma from recovered COVID-19 patients.
The antibody cocktail evaluated by UMSOM researchers is being used to treat COVID-19 patients in a clinical trial that was launched in June.
To produce the monoclonal antibodies to fight COVID-19, the researchers needed to identify which antibodies fight the novel coronavirus most effectively.
This involved determining which could bind most effectively to the spike protein found on the surface of SARS-CoV-2. The team evaluated thousands of human antibodies from plasma donations from recovered COVID-19 patients. They also generated antibodies from mice genetically engineered to produce human antibodies when infected.